Your Location:Home >Products >API >128794-94-5

Product Details
|
Description |
Mycophenolate mofetil was launched in 1995 in the U.S.A., its first market worldwide, for the prevention of acute kidney transplant rejection in conjunction with other immunosuppressive therapy and to treat refractory acute kidney graft rejection. With improved oral absorption and bioavailability, mycophenolate mofetil is a prodrug of mycophenolic acid (MPA), a fermentation product of several Penicillium species. MPA is a selective, reversible, non-competitive inhibitor of inosinate dehydrogenase and guanylate synthetase. It inhibits the de now pathway of purine biosynthesis. MPA was found to have more potent antiproliferative effects on T and B lymphocytes than other cell types. Compared with other immunosuppressants, mycophenolate mofetil is reportedly superior due to its unique mechanism of action and excellent safety profile for long term use. Mycophenolate mofetil is being investigated clinically in the treatment of heart and liver transplantation rejection, asthma, in preventing coronary artery restenosis, and in treating rheumatoid arthritis. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White Powder |
|
Originator |
Roche (Switzerland) |
|
Uses |
An immunosuppressant. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A carboxylic ester resulting from the formal condensation between the carboxylic acid group of mycophenolic acid and the hydroxy group of 2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethanol. In the liver, it is metabolised to mycophenolic acid, an immunosuppressant for which it is prodrug. It is widely used to prevent tissue rejection following organ transplants as well as for the treatment of certain autoimmune diseases. |
|
Indications |
Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF, CellCept) is an ester prodrug of mycophenolic acid (MPA), a Penicillium-derived immunosuppressive agent that blocks de novo purine synthesis by noncompetitively inhibiting the enzyme inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase. MPA preferentially suppresses the proliferation of cells, such as T and B lymphocytes, that lack the purine salvage pathway and must synthesize de novo the guanosine nucleotides required for DNA and RNA synthesis.MPA has been used for decades as a systemic treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis. MMF was developed to increase the bioavailability of MPA. |
|
Brand name |
CellCept |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Mycophenolate mofetil is a prodrug of mycophenolic acid (Cat. # M5255) that is cleaved by nonspecific esterases in vivo to produce the parent compound. Mycophenolic acid blocks inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase and is a potent immunosuppresive agent. |
|
Mechanism of action |
the guanosine nucleotides required for DNA and RNA synthesis.MPA has been used for decades as a systemic treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis. MMF was developed to increase the bioavailability of MPA. |
|
Clinical Use |
MMF is indicated for the prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving renal, hepatic, and cardiac transplants; it is often used in combination with other immunosuppressive agents for this indication. In dermatology, MMF is particularly useful as monotherapy, or as a steroid-sparing agent, for treatment of autoimmune blistering diseases (bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus). It may also be useful for the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases mediated by neutrophilic infiltration, such as pyoderma gangrenosum, and psoriasis. |
|
Side effects |
Adverse effects produced by MMF most commonly include nausea, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and possibly an increased incidence of viral and bacterial infections. Whether MMF may be associated with an increased long-term risk of lymphoma or other malignancies is controversial; however, any such risk is likely to be lower in patients treated for skin disease with MMF monotherapy than in transplant patients treated with combination immunosuppressive therapy. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine (increased risk of agranulocytosis). Antivirals: higher concentrations of both mycophenolate and aciclovir or ganciclovir when the two are prescribed concomitantly. Antacids: absorption of mycophenolate decreased in presence of magnesium and aluminium salts. Antibacterials: bioavailability of mycophenolate possibly reduced by metronidazole and norfloxacin; concentration of active metabolite reduced by rifampicin. Colestyramine: 40% reduction in oral bioavailability of mycophenolate. Ciclosporin: some studies show that ciclosporin decreases plasma MPA AUC levels; other studies show increases - no dose change required. Iron preparations: may significantly reduce absorption of mycophenolate. Sevelamer: reduced levels of mycophenolate. Tacrolimus: increases MPA concentrations- no dose change required but monitor closely. See 'Other information' |
|
Metabolism |
Mycophenolate undergoes presystemic metabolism in the liver to active mycophenolic acid (MPA). MPA undergoes enterohepatic recirculation and secondary increases in plasma MPA concentrations are seen; these have been reported at between 6-12 hours after a dose of mycophenolate mofetil, and at between 6-8 hours after a dose of mycophenolate sodium. MPA is metabolised by glucuronidation to the inactive mycophenolic acid glucuronide. The majority of a dose of mycophenolate is excreted in the urine as this glucuronide, with negligible amounts of MPA; about 6% of a dose is recovered in faeces. |
InChI:InChI=1/C23H31NO7/c1-15(5-7-19(25)30-13-10-24-8-11-29-12-9-24)4-6-17-21(26)20-18(14-31-23(20)27)16(2)22(17)28-3/h4,26H,5-14H2,1-3H3
The present invention provides a method ...
The present invention provides a method ...
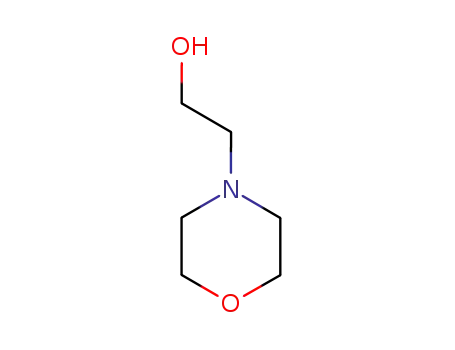
2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethanol
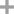
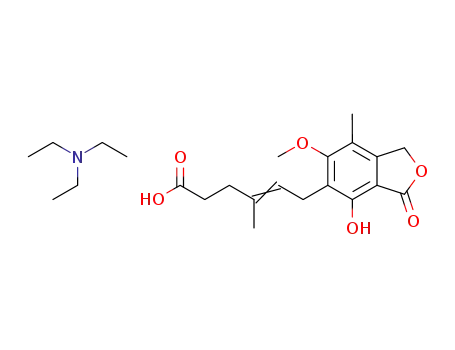
mycophenolic acid triethylamine salt

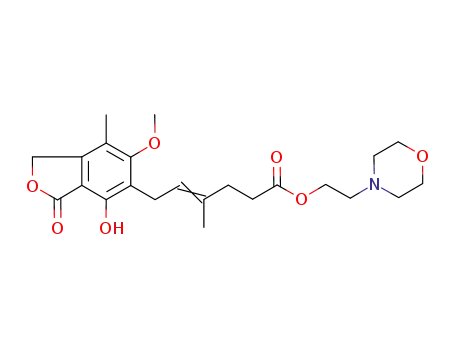
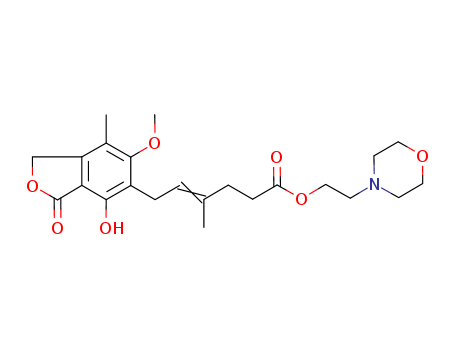
mycophenolate mofetil
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethanol; mycophenolic acid triethylamine salt; In o-xylene; at 110 - 120 ℃; for 44 - 47h; pH=6.8 - 7.3;
With sulfuric acid; In o-xylene; water; at 20 - 28 ℃; pH=2.0 - 7.3;
With sodium hydroxide; In water; ethyl acetate; pH=8.0; Product distribution / selectivity;
|

2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethanol


mycophenolic acid triethylamine salt

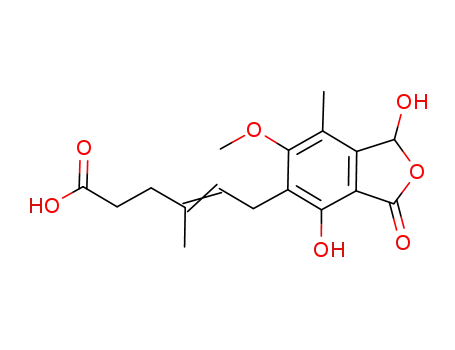
MPA-OH


mycophenolate mofetil

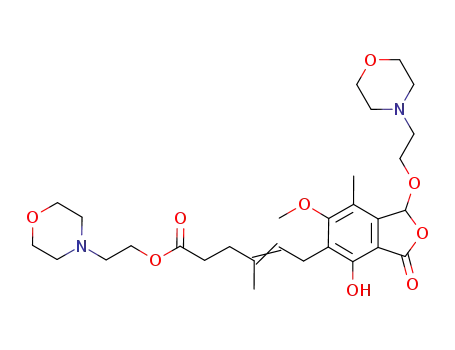
C29H42N2O9
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In xylene; at 120 - 125 ℃; for 3 - 71h; Conversion of starting material;
|

2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethanol

MPA-OH
CAS:2941-78-8
CAS:1143516-05-5
CAS:274693-27-5
CAS:120202-66-6